Table Of Contents
Equity Market Meaning
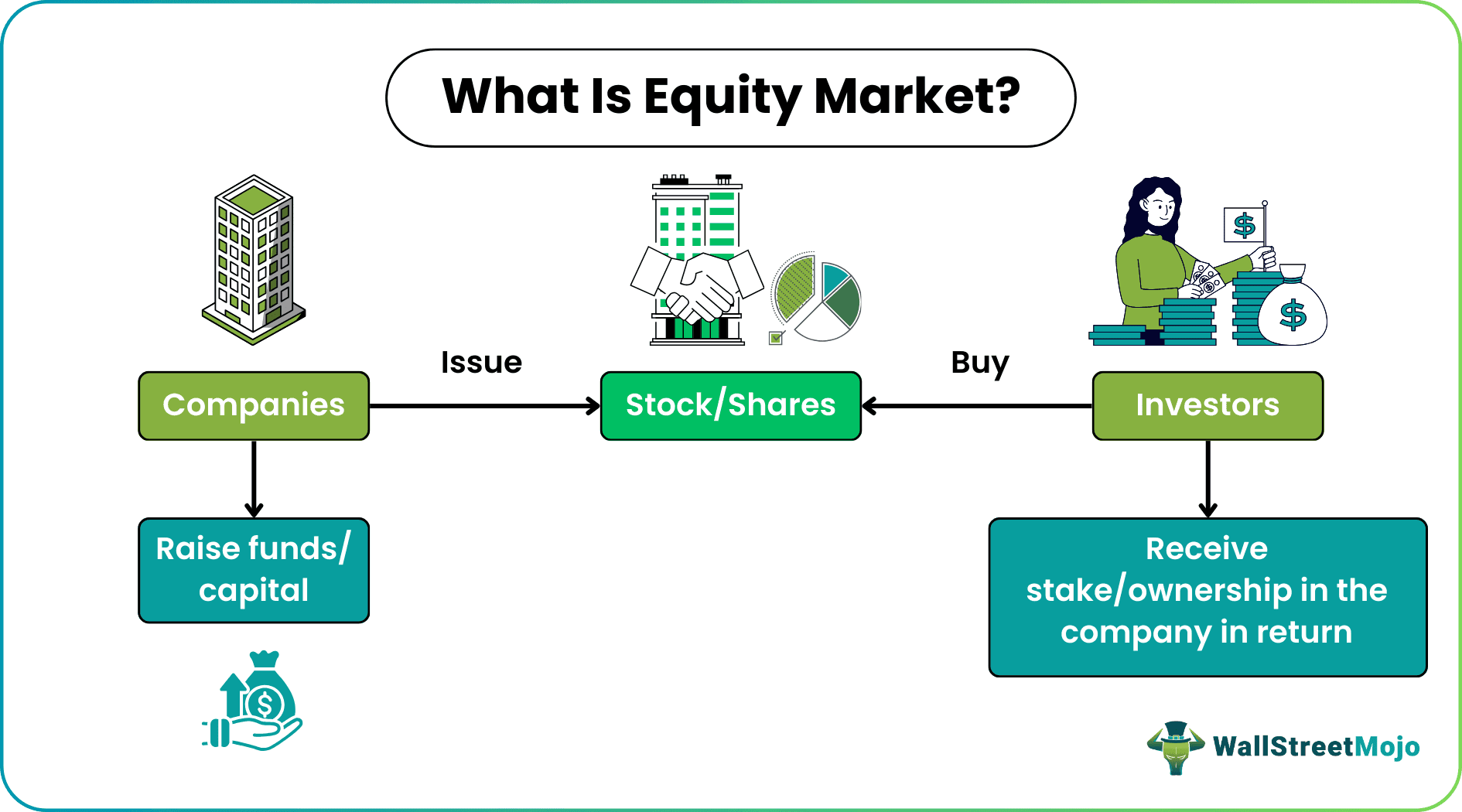
The equity market refers to the platform where companies issue shares for sale and investors buy them, helping the former raise capital for enhancing business growth and opportunities. It gives the investors a proportionate stake in the company; hence, they gain ownership of the firm through the shares they purchase.
An equity market is synonymous with stock market. These stocks are bought and sold either via a stock exchange or over-the-counter (OTC) market. Here, the sale and purchase occur at a specific price. This is the price at which the buyer agrees to buy, and the seller agrees to sell.
Key Takeaways
- The equity market refers to the marketplace where stocks/shares are bought and sold between companies and investors.
- The exchange helps companies raise funds for further growth and investors to have a stake in them, giving them ownership rights.
- Primary and secondary markets are two types of equity markets.
- These markets indicate the country's pulse and employs funds of the majority of social security initiatives.
How Does Equity Market Work?
The equity market connects the buyers and sellers having the same price expectations. As soon as the companies establish themselves, they become a private player in the corporate sector. Then, they issue shares as an Initial Public Offering (IPO). This makes their assets accessible to the public investors, who keep a check on the stock exchanges for the best stock deals for the day.
In their nascent stage, the companies, through this equity or stock market, get an opportunity to raise funds and utilize them to grow their business. On the other hand, the investors who provide those funds receive a stake in the firms, enjoying an ownership right simultaneously. As time passes, they realize the firms' potential to grow and reap profit. Hence, it becomes easier for these angel investors to decide whether they would like to continue the collaboration and increase their share in the company.
When companies enter the global equity market and list their shares through an IPO, they get listed on the stock exchanges. Then, based on the budgets, the buyers and sellers connect. In short, the trade takes place only when the price requirements match. The buying and selling of the stocks occur either through the stock exchanges, which are a centralized platform, or an OTC market where a broker matches the deals based on the price the buyer want to buy and the seller wants to sell the shares.
The most popular stock exchanges are New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), NASDAQ, London Stock Exchange, Bombay Stock Exchange, etc.
Many traders use Saxo Bank International to research and invest in stocks across different markets. Its features like SAXO Stocks offer access to a wide range of global equities for investors.
Types of Equity market
The equity market is classified into two categories – primary and secondary markets.
Primary Market
Also referred to as the issue market, this is the place where companies introduce or issue their equity market shares for the very first time. The companies can publicly give the shares as an IPO or through a Follow on Public offer (FPO). They can also consider rights issues, allowing their existing shareholders to maintain their earlier ratio in the shares and sell securities at a price lower than the current market prices.
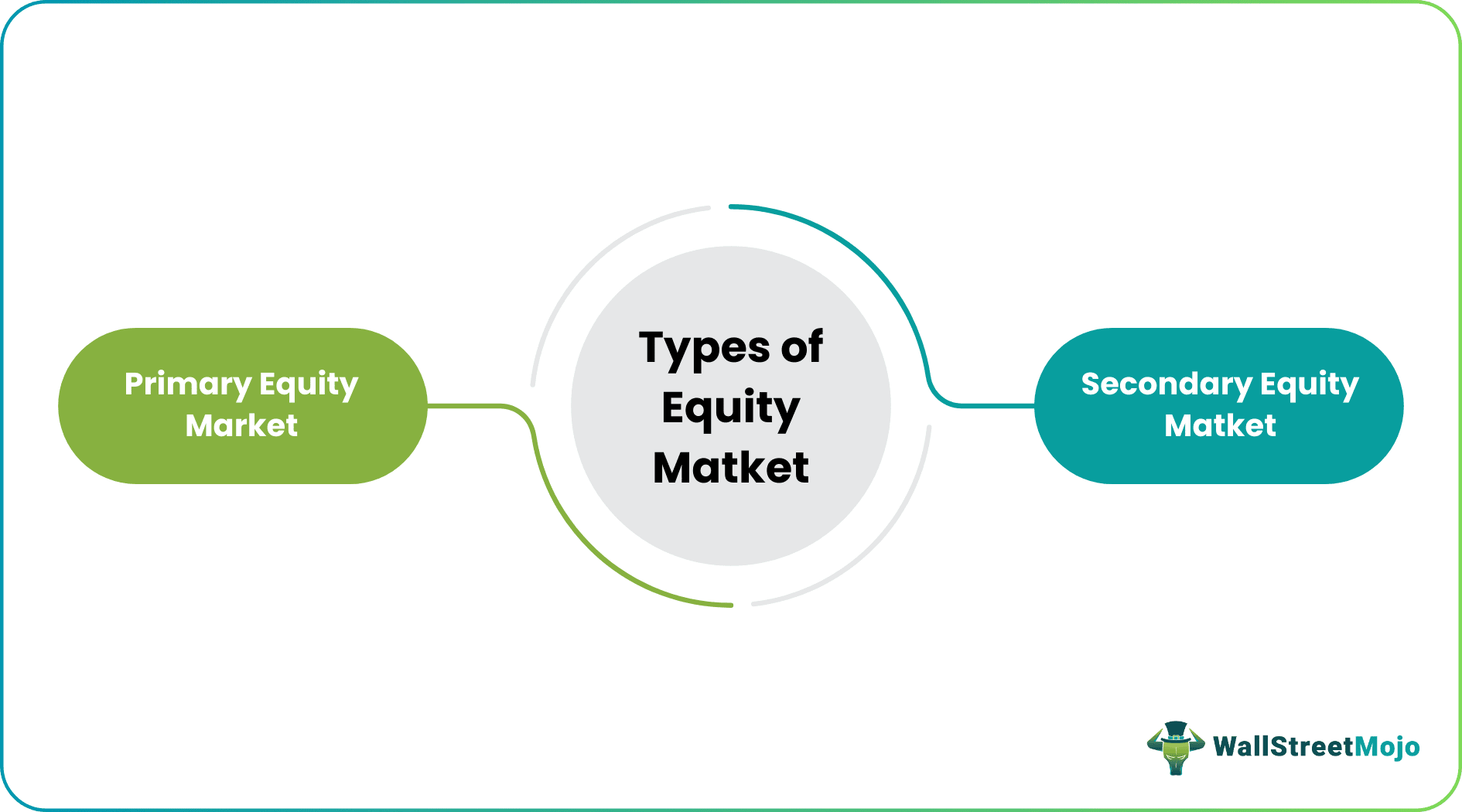
Secondary Market
As soon as the securities are put on sale after their first time, they are said to enter the secondary market, where they move from the hands of one investor to another. The securities of semi-government bodies, government organizations, joint-stock companies, etc. trade under this market category. It is for the investors who are into daily trading.
Features
The equity market makes companies allow investors to enjoy ownership in exchange for capital. As a result, the former get financial benefits, and the latter has ownership rights. Besides that, the stock market also helps raise capital for companies, and enhance liquidity and investment opportunities to boost the economy.
When the companies are budding, they issue shares for interested investors to buy. These investments from various sources help build their capital, thereby letting them think about the further growth of the business. The investors' decision is completely based on the business idea one has. If the concept is convincing, the investors are ready to invest in them to check if there is room for potential growth.
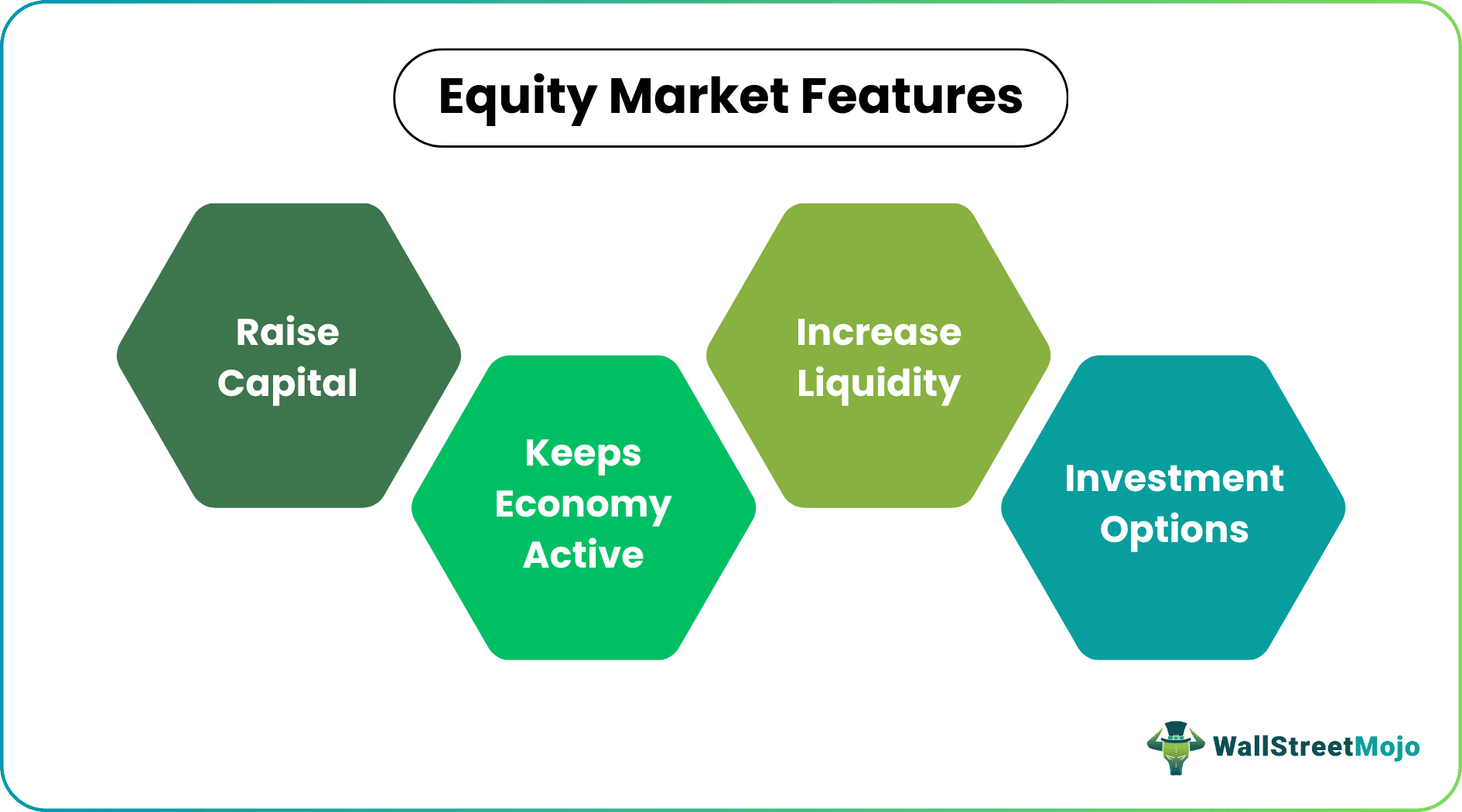
Secondly, it turns a market liquid, indicating the easy conversion of assets into cash. These markets are centralized platforms where the prices at which buyers and sellers want to deal in security are matched. Based on this match, the trade takes place, converting the securities into instant cash. The demand and supply of assets are quick enough, which keeps the market active throughout the day.
The third one on the list is enhanced investment options. Investors get an opportunity to have their own choices. They can work on the risks associated with the deal and be available for different deals in a row. They have full liberty to choose the companies, the securities of which they think would be more fruitful.
The above features reflect how important a world equity market is to ensure the stability of a country's economy as the market is active and stable.
Example
In the US equity market, the most dominant player is the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), hosting a hybrid stock exchange option. It means it acts as a physical exchange as well as provides scope for online deals as well. NYSE is the largest global equity-focused exchange based on the total capitalization of stocks listed there. It was held privately till 2005 and went public after acquiring Archipelago (a trading exchange working in electronic mode) and Euronext (Europe's largest exchange). Currently, the ownership of the NYSE is held by an American public company, Intercontinental Exchange.
Debt vs Equity Market
The debt market is a platform where assets are traded. On the contrary, an equity market is a junction where securities are traded. Debt instruments include bonds and mortgages requiring fixed installment payments with interest, while equity instruments include stocks/shares.
Dealing in an equity market never makes companies indebted. On the contrary, a debt instrument, when issued to borrowers, increases their debt liability. In equity financing, the funds help raise capital in exchange for ownership rights to investors. In contrast, debt financing is all about borrowing finances only to repay sources, adding the interest charges to the principal amount.
Though the equity market is riskier than the debt market, investors still prefer dealing there for a highly rewarding option.
Disclosure: This article contains affiliate links. If you sign up through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The equity market, also known as the stock market, is a platform where shares are issued and exchanged between companies and investors to raise funds for the organizations. For investors, who buy those shares, the stock market opens up a window to invest in a growing company by sharing/enjoying ownership rights in the firms in exchange for their investment.
The companies issue shares and get listed with the stock exchanges in the region. If they find the business idea convincing, the interested investors invest in the stocks of the firms. Besides listing themselves with the stock exchanges, they can go for over-the-counter (OTC) deals. Here, a broker remains involved to match the requirements of buyers and sellers for the trade to occur.
This market is quite volatile. Of course, it's rewarding when things go well, but the price fall has an adverse effect on the company. In equity financing, while the company receives funds for further growth, the investors get ownership rights in the firm and keep a watch on its progress. If the growth is significant, they remain collaborated for a longer period.

